Core Concepts
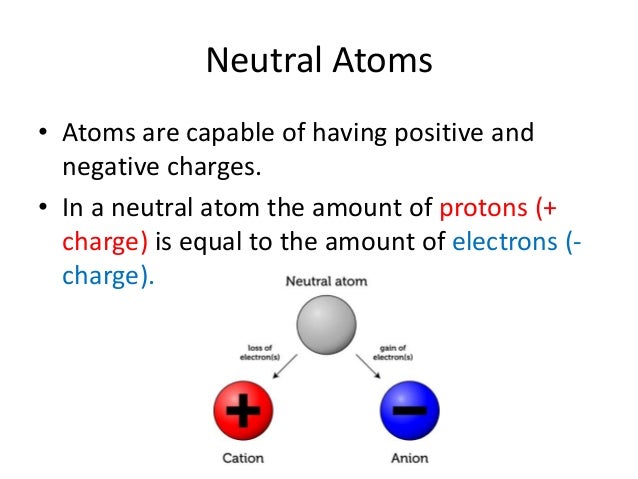
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons. *
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of What
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
In this tutorial, you will learn how to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. In addition, you will learn about the different subatomic particles. If you enjoy this tutorial, be sure to check out our others!
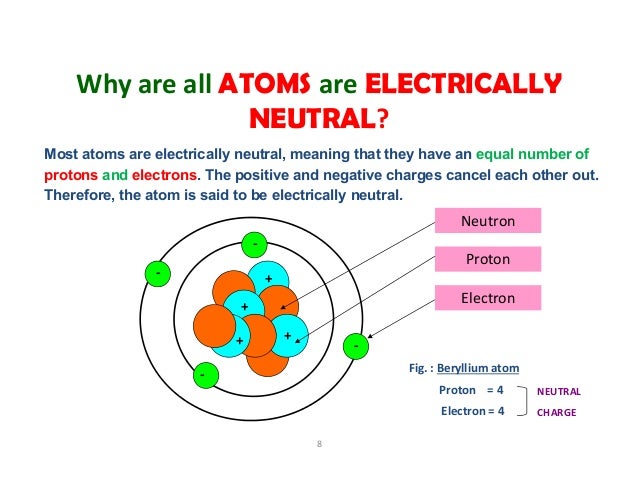
And by definition the atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in it. So the atomic number of a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons or the number of electrons in the atom. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Neon is 10. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom. In a neutral atom, the number of protons are equal to the number of electrons.
Covered in other articles
Vocabulary:
- Protons: Positively charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic Mass: Number of neutrons and protons present.
- Atomic Number: Number of protons present in an atom.
Finding the Number of Protons
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, let’s use oxygen. According to the periodic table, oxygen has the atomic number eight. The atomic number is located above the element’s symbol. Since oxygen has an atomic number of eight, there must be eight protons total. Moreover, the number of protons never changes for an element.
Finding the Number of Neutrons
The number of neutrons in an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass. Both of these numbers can be found on the periodic table. The atomic number is listed above the symbol of the element whereas the mass number is placed below. Let’s keep using oxygen as our example. Its atomic mass is 15.999 atomic mass units (amu) and its atomic number is 8. When we subtract 8 from 15.999, we will get 8. Also, it should be noted that the number of neutrons for an element may vary. Some elements have isotopes, which have different masses and therefore different numbers of neutrons.
Finding the Number of Electrons
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of an element. This means the number of electrons and the number of protons in an element are equal. Therefore, the number of electrons in oxygen is 8. Moreover, since these two subatomic particles, electrons and protons, have opposite charges, they cancel out and keep the atom neutral.
Summary Table
Further Reading
| Fundamental Subatomic Particles | Electromagnetic Radiation |
| Light and Other Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation | |
| Particle | Symbol | Charge | Mass | |
| electron | e- | -1 | 0.0005486 amu | |
| proton | p+ | +1 | 1.007276 amu | |
| neutron | no | 0 | 1.008665 amu | |
The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom can be determined from a set of simple rules.
- The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom is equal to the atomic number (Z).
- The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
- The mass number of the atom (M) is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- The number of neutrons is equal to the difference between the mass number of the atom (M) and the atomic number (Z).
Examples: Let's determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following isotopes.
The different isotopes of an element are identified by writing the mass number of the atom in the upper left corner of the symbol for the element. 12C, 13C, and 14C are isotopes of carbon (Z = 6) and therefore contain six protons. If the atoms are neutral, they also must contain six electrons. The only difference between these isotopes is the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
12C: 6 electrons, 6 protons, and 6 neutrons
13C: 6 electrons, 6 protons, and 7 neutrons
14C: 6 electrons, 6 protons, and 8 neutrons
| Practice Problem 1: Calculate the number of electrons in the Cl- and Fe3+ ions. |
Much of what is known about the structure of the electrons in an atom has been obtained by studying the interaction between matter and different forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation has some of the properties of both a particle and a wave.
Particles have a definite mass and they occupy space. Waves have no mass and yet they carry energy as they travel through space. In addition to their ability to carry energy, waves have four other characteristic properties: speed, frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. The frequency (v) is the number of waves (or cycles) per unit of time. The frequency of a wave is reported in units of cycles per second (s-1) or hertz (Hz).
The idealized drawing of a wave in the figure below illustrates the definitions of amplitude and wavelength. The wavelength (l) is the smallest distance between repeating points on the wave. The amplitude of the wave is the distance between the highest (or lowest) point on the wave and the center of gravity of the wave.
If we measure the frequency (v) of a wave in cycles per second and the wavelength (l) in meters, the product of these two numbers has the units of meters per second. The product of the frequency (v) times the wavelength (l) of a wave is therefore the speed (s) at which the wave travels through space.
vl = s
| Practice Problem 2: What is the speed of a wave that has a wavelength of 1 meter and a frequency of 60 cycles per second? |
| Practice Problem 3: Orchestras in the United States tune their instruments to an 'A' that has a frequency of 440 cycles per second, or 440 Hz. If the speed of sound is 1116 feet per second, what is the wavelength of this note? |
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons. *
Light is a wave with both electric and magnetic components. It is therefore a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Visible light contains the narrow band of frequencies and wavelengths in the portion of the electro-magnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect. It includes radiation with wavelengths between about 400 nm (violet) and 700 nm (red). Because it is a wave, light is bent when it enters a glass prism. When white light is focused on a prism, the light rays of different wavelengths are bent by differing amounts and the light is transformed into a spectrum of colors. Starting from the side of the spectrum where the light is bent by the smallest angle, the colors are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
As we can see from the following diagram, the energy carried by light increases as we go from red to blue across the visible spectrum.

Because the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation can be as long as 40 m or as short as 10-5 nm, the visible spectrum is only a small portion of the total range of electromagnetic radiation.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio and TV waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, g-rays, and cosmic rays, as shown in the figure above. These different forms of radiation all travel at the speed of light (c). They differ, however, in their frequencies and wavelengths. The product of the frequency times the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is always equal to the speed of light.
vl = c
As a result, electromagnetic radiation that has a long wavelength has a low frequency, and radiation with a high frequency has a short wavelength.
| Practice Problem 4: Calculate the frequency of red light that has a wavelength of 700.0 nm if the speed of light is 2.998 x 108 m/s. |
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of What
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
