Atomic Number of Hydrogen is 1.
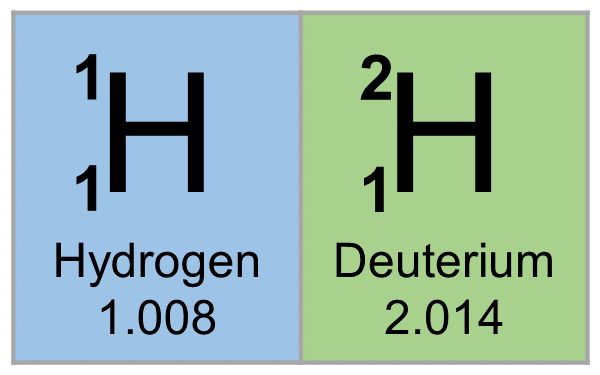
The mass number (also called 'atomic mass index') is the total of the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. Hydrogen usually has one proton and no neutrons. Other isotopes contain one or even two neutrons, but these are usually called by the special names deuterium and tritium. Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. Neutron Number and Mass Number of Hydrogen Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Hydrogen are 1; 2.
Chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. Number of protons in Hydrogen is 1. Atomic weight of Hydrogen is 1.008 u or g/mol. Melting point of Hydrogen is -259,1 °C and its the boiling point is -252,9 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery Year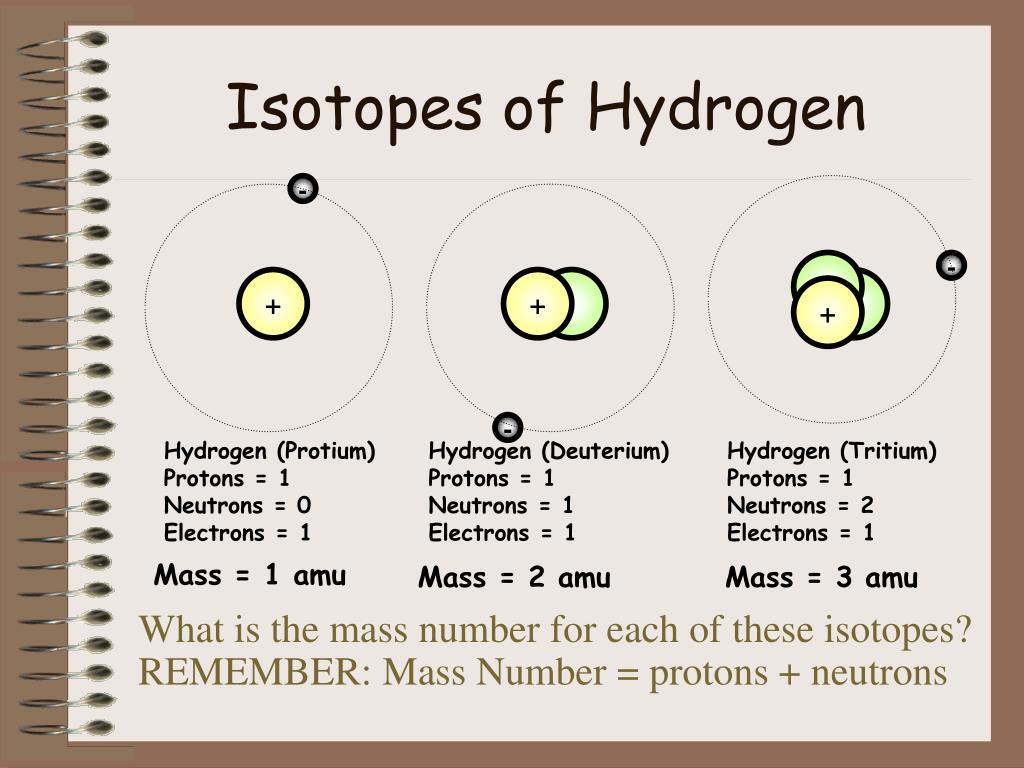
About Hydrogen
Known as the most abundant and the lightest chemical element in our Universe, hydrogen is a type of gas without color and smell, which also has the lowest density of all gases. It is believed to be the first atom produced in our Universe after the Big Bang, and all other elements were further produced from hydrogen as a result of nuclear fusion. The name of the gas is formed from two Greek words, meaning water and forming, so this is the element which creates water. Since hydrogen is a part of water molecule, it is an absolutely essential chemical element for life, which can be found in all living bodies on our planet. It is extensively used in a large variety of industrial branches, from chemical industry (producing fertilizers, etc) to electronic (substance producing) and food industry, etc. One more very important point is: hydrogen is now seen as a source of clean eco-friendly fuel of the future, which will help the humanity to solve the problem of pollution and being gas/oil dependent.
Uses of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is mostly used in the petroleum and chemical industries. The most important use of hydrogen in the world is in ammonia manufacture for the fertilizer market. The other significant use of this chemical element is in fossil fuel processing. Today, liquid hydrogen is used as a primary fuel of the American space program by The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Hydrogen is also used in various industrial fields such as metalworking and as a coolant in generators in power stations.
Compounds with Hydrogen
- H2O = Water (2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen)
- CH4 = Methane (1 carbon, 4 hydrogen)
- NH3 = Ammonia (1 nitrogen, 3 hydrogen)
- C6H12O6 = Glucose
- C9H8O4 = Aspirin
- NaHCO3 = Baking Soda
- C2H6O = Alcohol
- C12H22O11 = Sugar
- CH3COCH3 = Acetone
- C3H8 = Propane
- C2H4O2 = Acetic Acid
- HCI = Hydrochloric Acid
- C6H8O6 = Ascorbic Acid
- C3H6O3 = Lactic Acid
- H2S = Hydrogen Sulfide
- C2H4O2 = Vinegar
- C2H6O = Ethanol
- C4H10 = Butane
- C12H22O11 = Sucrose
- H2O2 = Hydrogen Peroxide
- NaOH = Sodium Hydroxide
- C6H6 = Benzene
- C10H16O = Camphor
- H2S = Hydrogen Sulfide
- CH3OH = Methanol
Properties of Hydrogen Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 1 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | H |
| Group | 1 |
| Period | 1 |
| Atomic Weight | 1.008 u |
| Density | 0.00008988 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 14.01 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | -259,1 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 20.28 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | -252,9 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 14.304 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 1400 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Gas |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Non-metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 2.2 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 13.59844 |
| Atomic Radius | 25pm |
| Covalent Radius | 38pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 120 |
| Valence Electrons | 1 |
| Year of Discovery | 1766 |
| Discoverer | Cavendish |
What is the Boiling Point of Hydrogen?
Hydrogen boiling point is -252,9 °C. Boiling point of Hydrogen in Kelvin is 20.28 K.
What is the Melting Point of Hydrogen?
Hydrogen melting point is -259,1 °C. Melting point of Hydrogen in Kelvin is 14.01 K.

How Abundant is Hydrogen?
Abundant value of Hydrogen is 1400 mg/kg.
What is the State of Hydrogen at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
State of Hydrogen is Gas at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.
When was Hydrogen Discovered?
Hydrogen Mass Number 2
Hydrogen was discovered in 1766.
Molar mass of H = 1.00794 g/mol
%2C_black_and_white.png?revision=2)
Convert grams Hydrogen to moles or moles Hydrogen to grams
| Symbol | # of Atoms | Hydrogen | H | 1.00794 | 1 | 100.000% |
Hydrogen Mass Number And Atomic Number
In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.
Hydrogen Mass Number
Finding molar mass starts with units of grams per mole (g/mol). When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula.
If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100.
Formula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights.
A common request on this site is to convert grams to moles. To complete this calculation, you have to know what substance you are trying to convert. The reason is that the molar mass of the substance affects the conversion. This site explains how to find molar mass.
Size Of Hydrogen Atom
Using the chemical formula of the compound and the periodic table of elements, we can add up the atomic weights and calculate molecular weight of the substance.
Periodic Table Hydrogen Mass Number
The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. We use the most common isotopes. This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes. For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass.
